Conditional Deployment Artifacts and Conditional Properties¶
This document holds a detailed step-by-step guide to deploy the enterprise plan of a web shop application to showcase conditional deployment artifacts and conditional properties, as presented in Figure 1. The motivating scenario is a simple shopping application that consists of a shop component and a database. Thereby, we take the role of a SaaS provider which offers different pricing plans to his customers. Furthermore, there are two different deployment artifacts: the community deployment artifact and the enterprise deployment artifact. The community deployment artifact implements the core functionality of the shop component whereas the enterprise deployment artifact additionally implements analytical reporting functionalities.
There is a free community plan that deploys the community deployment artifact along with SQLite on a small virtual machine. In contrast, the business plan is a paid plan that deploys the enterprise deployment artifact which contains analytical reporting functionalities along with MySQL on Google Cloud Platform (GCP). However, to have full access to all analytical reporting functionalities, the enterprise plan is required. An important aspect of the deployment of the shop component is that the correct SQL dialect must be configured.

Requirements¶
We need to fulfill the following requirements to follow this step-by-step guide.
- Ubuntu 22.04
- Access to a GCP project
- GCloud
- Git
- Unfurl
- Terraform
Preparation¶
First, we install OpenTOSCA Vintner. For more information see Installation.
Next, we configure Unfurl as the orchestrator that should be used for the deployment. For more information see Orchestrators.
Import the Template¶

First, we clone the repository.
Next, we import the template and initialize an instance.
Next, we initialize an application instance.
We can optionally inspect the Variability4TOSCA template. This template contains all possible elements having conditions assigned. For example, the MySQL database has a condition assigned that checks if the enterprise deployment artifact is present. An overview is given in Figure 2.
Resolve Variability¶
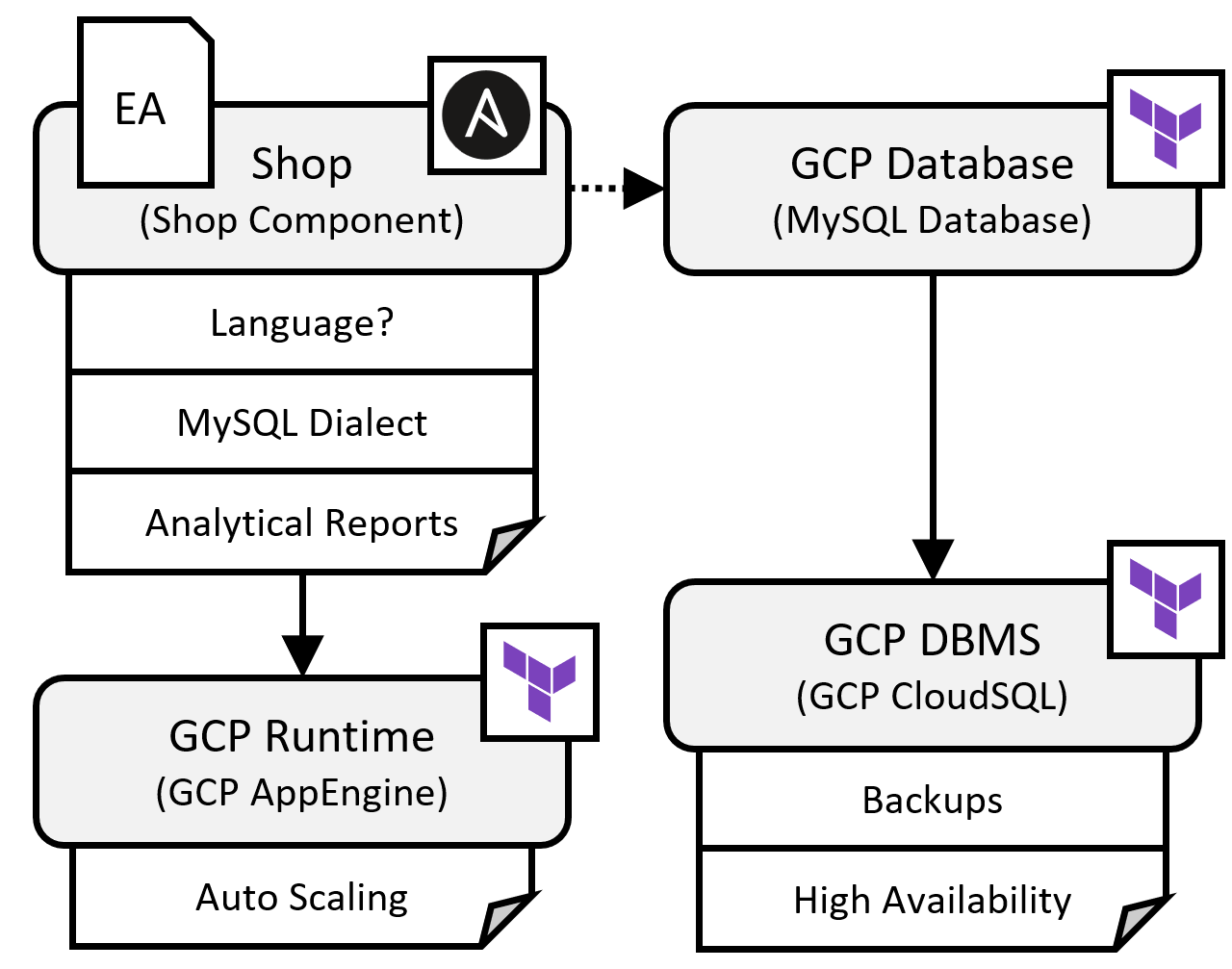
We intend to deploy the enterprise plan. Furthermore, we want to configure the display language of the shop component to be German. We specify this when resolving variability.
We can optionally inspect the generated TOSCA-compliant template. This template contains only the elements required for the enterprise plan. Notably, the enterprise deployment artifacts is present and configured to use the MySQL dialect. An overview is given in Figure 3.
Deploy the Application¶
Finally, we deploy the application.
Therefore, we need to provide deployment inputs, e.g., credentials to GCP.
Possible deployment inputs are specified in topology_template.inputs of the TOSCA-compliant template.
The deployment will take around 15-20 minutes.
Undeploy the Application¶
Afterward, we can undeploy the application.
Optionally, we can remove the instance and cleanup the filesystem. Cleaning up the filesystem removes any data including, e.g., all imported templates and created instances.
Complexity Analysis¶
The templates for our complexity analysis can be found here.
Logs¶
This deployment is also executed in our integration pipeline, which is executed once a week. The logs of the corresponding GitHub action can be accessed here. Relevant jobs start with "Unfurl Artifacts". Note, a GitHub account is required to access these logs. The raw logs are available without requiring an GitHub account.
Zenodo¶
The assets of this guide can be also found on Zenodo.
Publication¶
This guide is part of our research paper published at the main track of the CoopIS 2023. Also, this guide is further extended by our demonstration paper which was published at the demo track at the CoopIS 2023. Also check our other publications.